GAN으로 유사한 이미지를 얻어내는 방법들은 많이 나와 있다. 수치 정형데이터도 GAN으로 새로 생성해 낼 수 있는데, 아래의 블로그를 참조하였다.
How to Develop a 1D Generative Adversarial Network From Scratch in Keras
Generative Adversarial Networks, or GANs for short, are a deep learning architecture for training powerful generator models. A generator model is capable of generating new artificial samples that plausibly could have come from an existing distribution of s
machinelearningmastery.com
모델은 무작위의 랜덤 값들을 생성해 내다가 점점 2차방정식에 부합하는 조합들만 생성하는 것이다. GAN의 원리는 아래의 포스팅을 참고한다. 즉 (x,x^2)에 해당하는 값들을 생성모델이 발생시킨다. (응? 그냥 곱해서 출력하면 된다고요?)
[영상인식] GAN과 AutoEncoder
GAN(Genrative Adverserial Network)과 AE(Auto Encoder) 둘다 Generative 계열의 모델이다. Generative(생성)하다는 말 그대로 임의로 학습한 결과값과 원본 데이터를 판별자(Discriminator)에 넣어 두 가지가 얼..
magoker.tistory.com
우선, 생성(generator) 모델과 분별(discriminator) 모델, 그리고 결합된 GAN모델을 구성한다. 분별자 모델은 실제 데이터와 가짜 데이터를 구별할 수 있도록 별도로 훈련시키고, GAN 모델에서는 생성하는 데이터가 분별자 모델을 통과했을 때 True에 가까워지도록 생성자 모델만 학습시킨다.
from numpy import zeros
from numpy import ones
from numpy import hstack
from numpy.random import rand
from numpy.random import randn
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from matplotlib import pyplot
# 생성 모델은 Generator와 Discriminator가 결합된 GAN 모델 학습 시에 학습되고,
# 가짜 Data를 만드는 과정에서 사용된다.
def define_generator(latent_dim, n_outputs=2):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(15, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='he_uniform', input_dim=latent_dim))
model.add(Dense(n_outputs, activation='linear'))
return model
# 분별 모델은 진짜 데이터의 Target값을 1로, 가짜 데이터의 Target값을 0으로 하여 학습 시킨다
# 학습된 모델은 GAN모델에서 생성자와 결합된다.
def define_discriminator(n_inputs=2):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(25, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='he_uniform', input_dim=n_inputs))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
# compile model
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
# 분별자는 따로 학습되고 있어 가중치를 업데이트 하지 않는다 (판별용으로만 사용)
# GAN 모델에서는 생성자의 가중치만 업데이트 한다.
def define_gan(generator, discriminator):
# make weights in the discriminator not trainable
discriminator.trainable = False
# connect them
model = Sequential()
# add generator
model.add(generator)
# add the discriminator
model.add(discriminator)
# compile model
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam')
return model
GAN 모델의 Summary는 아래와 같다. 임의로 숫자를 발생시켜 2차원의 데이터를 만들고, 생성된 2차원의 데이터가 실제 데이터에 가까운지 판별하게 된다.
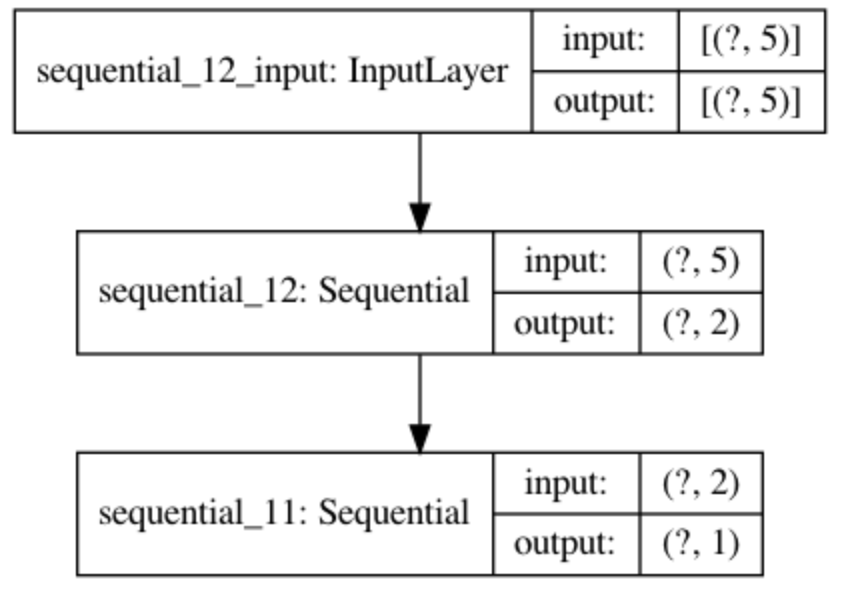
다음은 실제 데이터와 가짜 데이터를 생성하는 부분이다. 생성된 데이터들로 GAN모델을 학습시키기만 하면 된다.
# 실제 데이터를 생성해 내는 부분 (X, X^2)의 값을 만들고 실제 데이터이므로 Target 값은 True로 둔다
def generate_real_samples(n):
# generate inputs in [-0.5, 0.5]
X1 = rand(n) - 0.5
# generate outputs X^2
X2 = X1 * X1
# stack arrays
X1 = X1.reshape(n, 1)
X2 = X2.reshape(n, 1)
X = hstack((X1, X2))
# generate class labels
y = ones((n, 1))
return X, y
def generate_latent_points(latent_dim, n):
# generate points in the latent space
x_input = randn(latent_dim * n)
# reshape into a batch of inputs for the network
x_input = x_input.reshape(n, latent_dim)
return x_input
# 가짜 데이터를 만드는 부분. GAN에서 학습되는 Generator로 가공의 값을 만들고
# Target은 가짜이므로 False로 둔다
def generate_fake_samples(generator, latent_dim, n):
# generate points in latent space
x_input = generate_latent_points(latent_dim, n)
# predict outputs
X = generator.predict(x_input)
y = zeros((n, 1))
return X,y
필요한 데이터는 모두 준비되었으므로, 분별자를 따로 학습 시키고, 학습된 분별자를 이용해 생성자의 가중치를 업데이트 하면 된다. 학습 시 fit() 함수가 아닌 train_on_batch()가 사용되었는데, 기능상의 차이는 없고 배치별로 학습할 때 사용한다고 보면 된다.
# 분별자 학습
def train_discriminator(model, n_epochs=1000, n_batch=128):
half_batch = int(n_batch / 2)
# run epochs manually
for i in range(n_epochs):
# generate real examples
X_real, y_real = generate_real_samples(half_batch)
# update model
model.train_on_batch(X_real, y_real)
# generate fake examples
X_fake, y_fake = generate_fake_samples(half_batch)
# update model
model.train_on_batch(X_fake, y_fake)
# evaluate the model
_, acc_real = model.evaluate(X_real, y_real, verbose=0)
_, acc_fake = model.evaluate(X_fake, y_fake, verbose=0)
print(i, acc_real, acc_fake)
# GAN 모델 학습
def train_gan(gan_model, latent_dim, n_epochs=10000, n_batch=128):
# manually enumerate epochs
for i in range(n_epochs):
# prepare points in latent space as input for the generator
x_gan = generate_latent_points(latent_dim, n_batch)
# create inverted labels for the fake samples
y_gan = ones((n_batch, 1))
# update the generator via the discriminator's error
gan_model.train_on_batch(x_gan, y_gan)
모든 함수 구성이 완료되었으므로 train을 시작하는 모듈과 중간 결과를 차트로 보여줄 수 있는 함수를 만들어 테스트 해 본다.
# 중간의 결과를 보여주는 부분으로 실제 데이터와 가짜 데이터를 임의로 하나씩 생성해 내어 분별자로 해당 데이터가
# 얼마나 진짜와 가까운 지(accuracy)를 출력하고 차트에 생성된 데이터를 표시함
def summarize_performance(epoch, generator, discriminator, latent_dim, n=100):
# prepare real samples
x_real, y_real = generate_real_samples(n)
# evaluate discriminator on real examples
_, acc_real = discriminator.evaluate(x_real, y_real, verbose=0)
# prepare fake examples
x_fake, y_fake = generate_fake_samples(generator, latent_dim, n)
# evaluate discriminator on fake examples
_, acc_fake = discriminator.evaluate(x_fake, y_fake, verbose=0)
# summarize discriminator performance
print(epoch, acc_real, acc_fake)
# scatter plot real and fake data points
pyplot.scatter(x_real[:, 0], x_real[:, 1], color='red')
pyplot.scatter(x_fake[:, 0], x_fake[:, 1], color='blue')
pyplot.show()
def train(g_model, d_model, gan_model, latent_dim, n_epochs=10000, n_batch=128, n_eval=2000):
# determine half the size of one batch, for updating the discriminator
half_batch = int(n_batch / 2)
# manually enumerate epochs
for i in range(n_epochs):
# 실제 데이터를 생성하고
x_real, y_real = generate_real_samples(half_batch)
# 가짜 데이터는 Generator의 Predict로 만들어 낸다
x_fake, y_fake = generate_fake_samples(g_model, latent_dim, half_batch)
# 분별자(discriminator)를 생성한 데이터로 학습하고
d_model.train_on_batch(x_real, y_real)
d_model.train_on_batch(x_fake, y_fake)
# prepare points in latent space as input for the generator
x_gan = generate_latent_points(latent_dim, n_batch)
# create inverted labels for the fake samples
y_gan = ones((n_batch, 1))
# GAN모델을 통해 Generator를 학습 시킨다.
gan_model.train_on_batch(x_gan, y_gan)
# 중간의 결과물들을 출력
if (i+1) % n_eval == 0:
summarize_performance(i, g_model, d_model, latent_dim)
# 함수를 호출해 모델을 정의하고 train 실행
latent_dim = 5
discriminator = define_discriminator()
generator = define_generator(latent_dim)
gan_model = define_gan(generator, discriminator)
train(generator, discriminator, gan_model, latent_dim)
10,000번의 epoch을 거치는 동안 모델들은 아래와 같이 실제 데이터와 유사하게 가짜 데이터를 출력하기 시작한다.
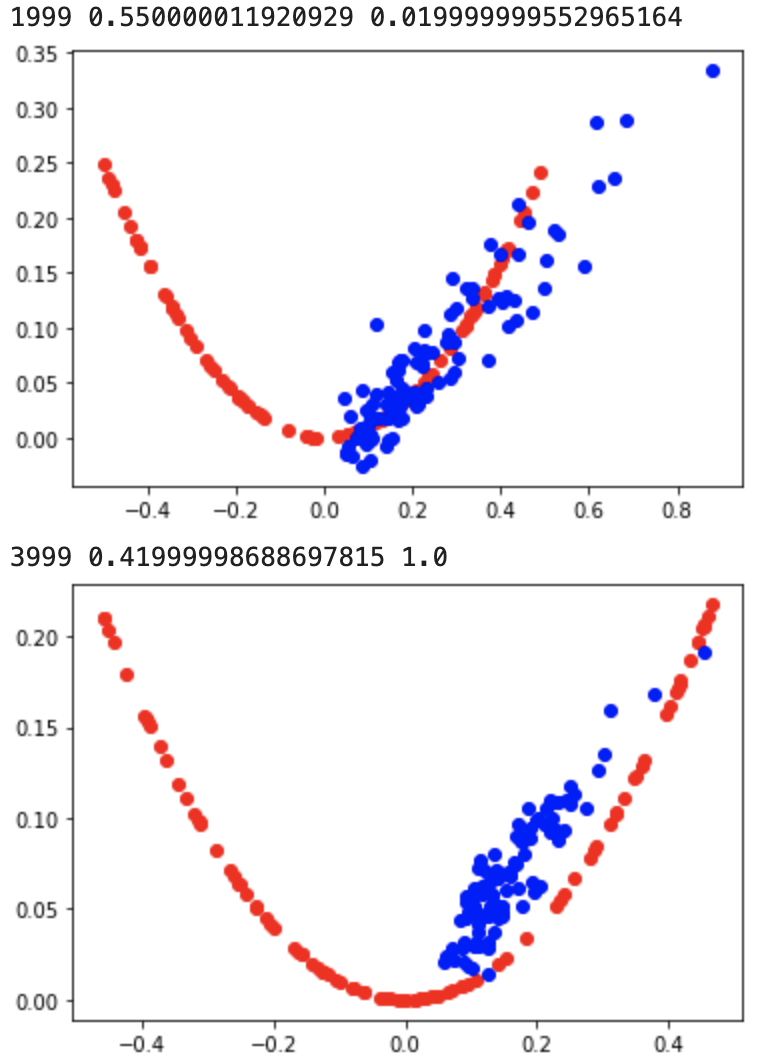
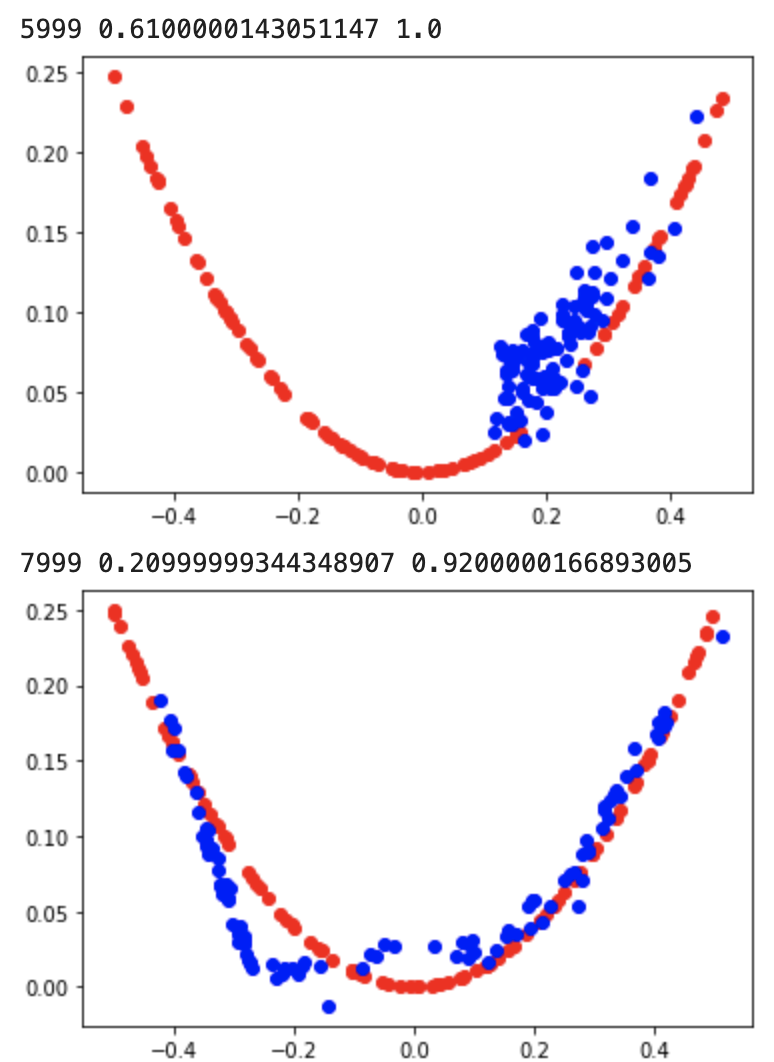
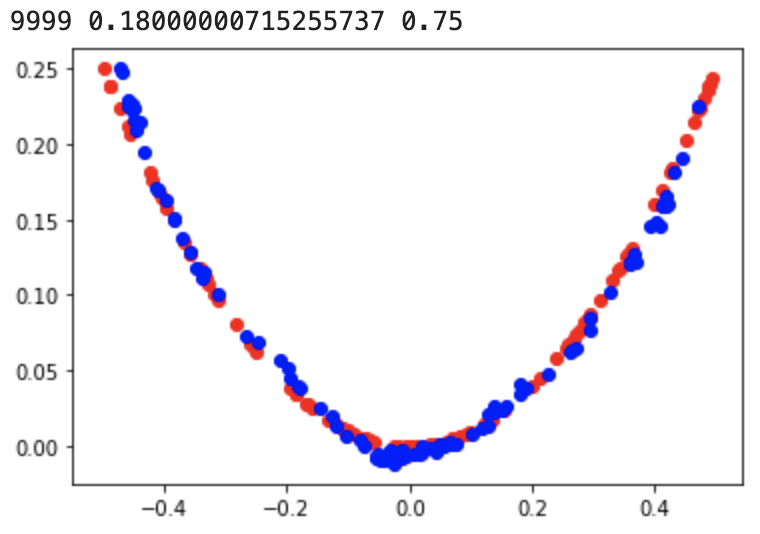
'AI 빅데이터 > 후려치는 데이터분석과 AI 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [데이터분석] Anomaly Detection을 위한 데이터 탐색 (0) | 2020.11.01 |
|---|---|
| [데이터분석] 주택가격 예측 Kaggle 도전기 (0) | 2020.09.25 |
| [데이터분석] 시계열 분석 3 - 딥러닝 (LSTM) (0) | 2020.09.10 |
| [데이터분석] 시계열분석 2 - XGBoost (1) | 2020.09.10 |
| [데이터분석] 시계열 분석 1 - ARIMA (937) | 2020.09.09 |




댓글